Yield Curve Inversion and its Economic Implications
Yield curve inversion occurs when short-term debt instruments have higher yields than long-term instruments of the same credit quality. In the United States, this typically refers to the relationship between the yields of US Treasury bonds with different maturities. When the yield curve inverts, it shows that investors are willing to accept lower returns (yield) on long-term bonds compared to short-term bonds, signaling a lack of confidence in the long-term economic outlook.
Historically, yield curve inversions have been reliable predictors of economic recessions in the United States. When the yield curve inverts, it suggests that investors anticipate a slowdown in economic
growth
and a potential decline in interest rates in the future. This is because investors tend to flock to the safety of long-term Treasury bonds during times of economic uncertainty, driving up their
prices
and pushing down their yields. Yields and prices are inversely related.
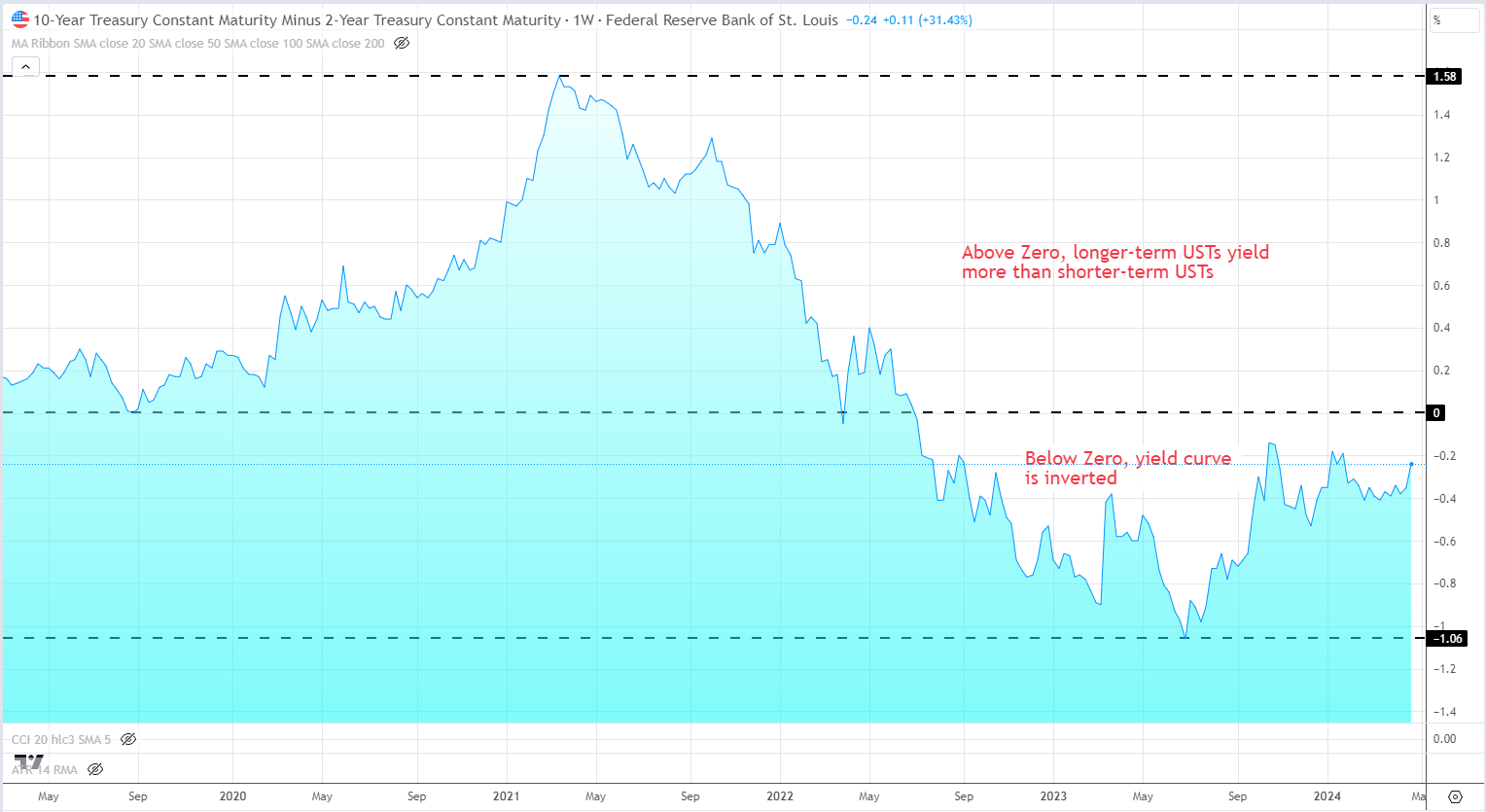
US Yield Curve – April 25, 2024
The most closely watched spread is between the 2-year and 10-year Treasury yields. When the 2-year yield rises above the 10-year yield, it is considered a significant warning sign for the economy. In the past, yield curve inversions have preceded recessions by an average of 18 to 24 months, although the timing can vary.
Learn How to Trade like a Professional with our Complimentary Guide
An inverted yield curve can have several implications for the US economy:
It is important to note that while yield curve inversions have been reliable recession indicators in the past, they do not guarantee that a recession will occur. Other economic factors, such as inflation, employment, and global trade, also play significant roles in shaping the economy's trajectory. Nevertheless, policymakers, businesses, and investors closely monitor the yield curve for signs of potential trouble on the horizon.
Foundational Trading Knowledge
Macro Fundamentals
Recommended by Nick Cawley
Start Course
Yield Curve Inversion and its Economic Implications